- When a ball is kicked past a goalpost, the goalpost—which is not in motion—is the reference point for the moving ball.
- For example, when a car is in motion, the ground is the reference point. In this setting, the ground is seen as not moving relative to the car.
- Relative motion is the calculation of the motion of an object with regard to some other moving or stationary object.
- Another example. A person sitting in an airplane is at zero velocity relative to the airplane, but is moving at the same velocity as the airplane with respect to the ground.
- The velocity of an object is the rate of change of its position with respect to a frame of reference, and is a function of time.
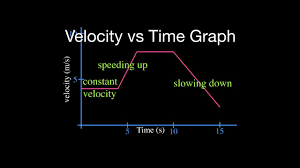
- Velocity is equivalent to an object's speed and direction of motion (e.g. 60 km/h to the north). Figure 1.
- Whether it's a car moving, a ball being dropped, or the earth moving around the sun, all of these things have their own velocity.
- Initial velocity describes how fast an object travels when gravity first applies force on the object.
- On the other hand, the final velocity is a vector quantity that measures the speed and direction of a moving body after it has reached its maximum acceleration.
- If an object starts from rest then it's initial velocity would be zero. Figure 2.
- However if it is already in motion then it does have an initial velocity of greater than zero. Figure 2.
- Displacement and velocity here.
Figure 1


No comments:
Post a Comment